
This is a guest repost by Venkatesh CM at Architecture Issues Scaling Web Applications.
I will cover architecture issues that show up while scaling and performance tuning large scale web application in this blog.
Lets start by defining few terms to create common understanding and vocabulary. Later on I will go through different issues that pop-up while scaling web application like
- Architecture bottlenecks
- Scaling Database
- CPU Bound Application
- IO Bound Application
Determining optimal thread pool size of an web application will be covered in next blog.
Performance
Term performance of web application is used to mean several things. Most developers are primarily concerned with are response time and scalability.
-
Response Time
Is the time taken by web application to process request and return response. Applications should respond to requests (response time) within acceptable duration. If application is taking beyond the acceptable time, it is said to be non-performing or degraded.
-
Scalability
The web application is said to be scalable if by adding more hardware, application can linearly take more requests than before. Two ways of adding more hardware are
- Scaling Up (vertical scaling) :– increasing the number CPUs or adding faster CPUs on a single box.
- Scaling Out (horizontal scaling) :– increasing the number of boxes.
Scaling Up Vs Scaling Out
Scaling out is considered more important as commodity hardware is cheaper compared to cost of special configuration hardware (super computer). But increasing the number of requests that an application can handle on a single commodity hardware box is also important. An application is said to be performing well if it can handle more requests with-out degrading response time by just adding more resources.
Response time Vs Scalability
Response time and Scalability don’t aways go together i.e. application might have acceptable response times but can not handle more than certain number of requests or application is handle increasing number of requests but has poor or long response times. We have strike a balance between scalability and response time to get good performance of the application.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning is an exercise of figuring out the required hardware to handle expected load in production. Usually it involves figuring out performance of application with fewer boxes and based on performance per box projecting it. Finally verifying it with load/performance tests.
Scalable Architecture
Application architecture is scalable if each layer in multi layered architecture is scalable (scale out). For example :– As shown in diagram below we should be able linearly scale by add additional box in Application Layer or Database Layer.
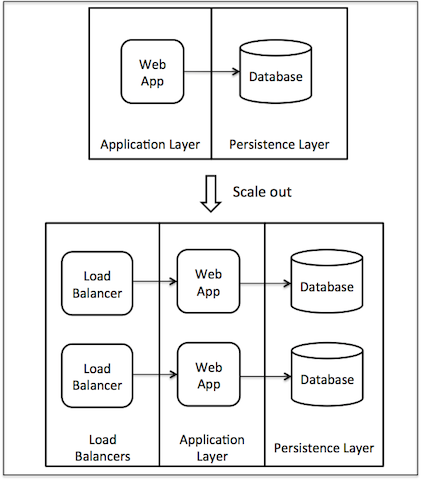
Scaling Load Balancer
Load balancers can be scaled out by point DNS to multiple IP addresses and using DNS Round Robin for IP address lookup. Other option is to front another load balancer which distributes load to next level load balancers.
Adding multiple Load balancers is rare as a single box running nginx or HAProxy can handle more than 20K concurrent connections per box compared to web application boxes which can handle few thousand concurrent requests. So a single load balancer box can handle several web application boxes.
Scaling Database
Scaling database is one of the most common issues faced. Adding business logic (stored procedure, functions) in database layer brings in additional overhead and complexity.
RDBMS
RDBMS database can be scaled by having master-slave mode with read/writes on master database and only reads on slave databases. Master-Slave provides limited scaling of reads beyond which developers has to split the database into multiple databases.
NoSQL
CAP theorem has shown that is not possible to get Consistency, Availability and Partition tolerance simultaneously. NoSql databases usually compromise on consistency to get high availability and partition.
Splitting database
Database can be split vertically (Partitioning) or horizontally (Sharding).
-
Vertically splitting (Partitioning) :– Database can be split into multiple loosely coupled sub-databases based of domain concepts. Eg:– Customer database, Product Database etc. Another way to split database is by moving few columns of an entity to one database and few other columns to another database. Eg:– Customer database , Customer contact Info database, Customer Orders database etc.
-
Horizontally splitting (Sharding) :– Database can be horizontally split into multiple database based on some discrete attribute. Eg:– American Customers database, European Customers database.
Transiting from single database to multiple database using partitioning or sharding is a challenging task.
Architecture Bottlenecks
Scaling bottlenecks are formed due to two issues
-
Centralised component A component in application architecture which can not be scaled out adds an upper limit on number of requests that entire architecture or request pipeline can handle.
-
High latency component A slow component in request pipeline puts lower limit on the response time of the application. Usual solution to fix this issue is to make high latency components into background jobs or executing them asynchronously with queuing.
CPU Bound Application
An application is said to be CPU bound if application throughput is limited by its CPU. By increasing CPU speed application response time can be reduced.
Few scenarios where applications could be CPU Bound
- Applications which are computing or processing data with out performing IO operations. (Finance or Trading Applications)
- Applications which use cache heavily and don’t perform any IO operations
- Applications which are asynchronous (i.e. Non Blocking), don’t wait on external resources. (Reactive Pattern Applications, NodeJS application)
In the above scenarios application is already working in efficiently but in few instances applications with badly written or inefficient code which perform unnecessary heavy calculations or looping on every request tend to show high CPU usage. By profiling application it is easy to figure out the inefficiencies and fix them.
These issues can be fixed by
- Caching precomputing values
- Performing the computation in separate background job.
IO Bound Application
An application is said to be IO bound if application throughput is limited by its IO or network operations and increasing CPU speed does not bring down application response times. Most applications are IO bound due to the CRUD operation in most applications Performance tuning or scaling IO bound applications is a difficult job due to its dependency on other systems downstream.
Few scenarios where applications could be IO Bound
- Applications which are depended on database and perform CRUD operations
- Applications which consume drown stream web services for performing its operations
Next blog will cover how to determining optimal thread pool size of an web application.